Excel activator and my latest VBA script
- 1. Prepare MS Excel to VBA programming.
- 2. My startup script.
- 3. Most important in VBA programming.
- 4. Going forward - call REST API.
- 5. Going forward - call Selenium driver.
- 6. Why script can not started.
- 7. Deploy VBA code.
- 8. Transform onPage VBA script to Excel Add-in.
- 9. Digital sign VBA code.

1. Prepare MS Excel to VBA programming.
I have included Microsoft as number one company what transformed internet to real hell on Earth Main internet companies what transformed internet to hell: Microsoft, Google, Payoneer, Paypal, Upwork, Freelancer, Linkedin, Huobi/HTX, Strip, Hetzner. therefore making damage to Microsoft is matter of honor for any programmers in whole world. Potentially, activation of any Microsoft product is job for couple of minutes. You need to deploy inactivated products in any Virtual machines like VmWare or KVM or VirtualBox or any other, then activate products than compare snapshots and you will receive changed files. You also can analyze request to MS frm Virtual Machine and response from MS. You even don't need know commands of IDA Pro (or any alternatives). For programmers cracking any Microsoft software this is just only challenge no more than one day, including all supporting operation.
But I have no time and wist to doing that ordinary job, because millions and millions programmers doing the same job just for fun - to punish fucking Microsoft company for all hell what that bastards doing. I have my own responsibility, I must create VBA script for customers, for himself I already used OpenOffice (the better choice then MS Office), but I can not influence to my customers which already like exactly the same functions, but not in free version (LibreOffice, OpenOffice and so on) and already want to paid money to Microsoft. Btw, if you need more advanced solution than Ms Office - looking to this my post LibreOffice - next generation of MS Excel and OpenOffice.
So, in this case I need only select correct solution from other programmers. And I selected this way - https://github.com/massgravel/Microsoft-Activation-Scripts?tab=readme-ov-file.
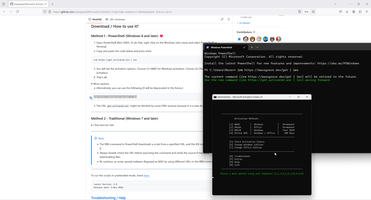
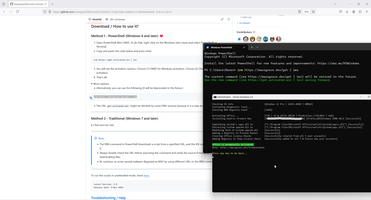
2. My startup script.
I made a lot of various VBA script, first script in my bog published in 2001 year VBA is the automation language of Excel. And time on time I publish various VBA code, for example:
- My typical Excel VBA project (Excel VBA frontend can working with remote database) + admin panel.
- Excel VSTO and DNA project templates.
Goal of my current script is prevent accept duplication data. So, if data repeat the previous data Excel refuse to accept data in active state.

As you can see on screen attempt to millions times entering data "31 32 33 32 36 39 39 35 30 30 30 30 37 30 30 35 46 42 36 32 31 35 36 36" ignored, only when new data is appear it accept by Excel.
Because fucking Microsoft already ban me, even in Github:
Therefore I will publish my last script in my blog.
1: Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
2: 'Debug.Print "Worksheet_Change";
3:
4: ' Disable events to prevent infinite loop
5: Application.EnableEvents = False
6:
7: On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
8:
9:
10: 'Debug.Print Target.Count, Target.Row, Target.Column
11: If Target.Count > 1 Then
12: Dim N As Integer, M As Integer
13: For N = 1 To Target.Row
14: For M = 1 To Target.Column
15: If Target.Cells(N, M) <> "" Then
16: HexDump (Target.Cells(N, M))
17: End If
18: Next M
19: Next N
20: Else
21: HexDump (Target.Value)
22: End If
23:
24:
25: Dim i As Long, initialRow As Long
26: initialRow = Target.Row
27:
28: For i = 1 To initialRow - 1
29: If Me.Cells(i, Target.Column) = Me.Cells(initialRow, Target.Column) And i <> initialRow Then
30: Target.ClearContents
31: Me.Cells(initialRow, Target.Column).Select
32: Exit For
33: Else
34: Me.Cells(initialRow, Target.Column) = Target.Value
35: Me.Cells(initialRow + 1, Target.Column).Select
36: End If
37: Next i
38:
39: IgnoreInput:
40: ' Re-enable events
41: Application.EnableEvents = True
42: Exit Sub
43: ErrorHandler:
44: Application.EnableEvents = True
45: If Err.Number <> 0 Then
46: Msg = "Error # " & Str(Err.Number) & " was generated by " _
47: & Err.Source & Chr(13) & "Error Line: " & Erl & Chr(13) & Err.Description
48: MsgBox Msg, , "Error", Err.HelpFile, Err.HelpContext
49: End If
50: Resume IgnoreInput
51: End Sub
52:
53 Public Function HexDump(ByVal text As String) As String
54 If text <> "" Then
55 Dim i As Long, charCode As Integer
56 Dim hexString As String
57 For i = 1 To Len(text)
58 charCode = AscW(Mid(text, i, 1))
59 hexString = hexString & Hex(charCode) & " "
60 Next i
61 Debug.Print (hexString)
62 End If
63 End Function
We can also place the same algorithm in the Workbook level:
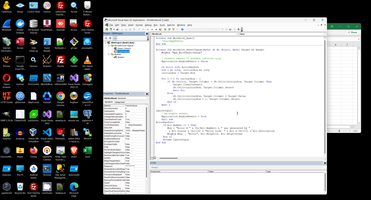
3. Most important in VBA programming.
This is very simple code, as you can see on screen above, this code prevent to store data if data repeat in another cell. But look to details:
- You need always use Description of Excel Object model and than Description of VBA operators what allow you manipulate with data in Object model.
- All code must have error handler (43-49) plus declaration on line 7
- Pay attention that variables must be usually Long, Integer this is Short value in VB.NET
- If we ignore Application.EnableEvents=true/false - we will receive infinity loop and Excel will block this script, because Me.Cells(I, Target.Column) Inside the loop fires this trigger again.
- Worksheet_Change is predefined name, already fires on each data changing on Worksheet, but not always !! What can prevent fires this trigger? This is most important place from VBA documentation:
- Events disabled: Application-level events might be disabled. Check if Application.EnableEvents is set to True. It's often good practice to temporarily disable events during macro execution to prevent infinite loops, but ensure they're re-enabled afterward.
- Manual calculation mode: If calculation mode is set to manual, the Worksheet_Change event might not trigger immediately. Try setting Application.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic.
- Protected sheet: If the worksheet is protected, the Worksheet_Change event might be blocked. Ensure the sheet is unprotected or that the "Allow users to edit ranges" option is enabled (if allowing changes to specific ranges is sufficient).
- Filtering: Changes made to filtered cells might not trigger the event reliably. Consider handling the Worksheet_Calculate event in conjunction with filtering to detect changes.
- Error handling: If an error occurs within the Worksheet_Change event procedure itself, subsequent changes might not be captured. Use proper error handling (e.g., On Error GoTo ...) to trap and address potential errors.
- Event procedure name mismatch: Double-check that the event procedure is named precisely Worksheet_Change. Even a slight typo can prevent it from being recognized.
- Incorrect scope: Ensure the code resides within the sheet module, not a standard module or class module. Double-click the sheet name in the VBA editor's Project Explorer to access the correct module.
- Shared workbook: Worksheet_Change can be unreliable in shared workbooks. Consider alternative approaches if working in a shared environment.
- Other event procedures interfering: Complex interactions between multiple event procedures can sometimes cause unexpected behavior. Review other event handlers in the workbook.
- Looping changes: If your code within Worksheet_Change makes further changes to the worksheet, it can trigger the event again, potentially leading to infinite loops. Use Application.EnableEvents = False strategically within the event handler if your code modifies the sheet. Remember to re-enable events with Application.EnableEvents = True after your changes are complete.
- String conversion operation:
- AscW gets the Unicode character code (integer representation) of the character.
- Hex(charCode) converts the character code to its hexadecimal representation (e.g., "41" for "A")
- Follow documentation, there are a number of way to change Active cell, my way in this project is not best optimized way, but simplest. You can see more efficient way in your project:
- Range.Select. This is the most straightforward method. You specify the range (cell or cells) you want to activate:
- Cells(row, column).Select. This method is useful when you want to select a cell based on its row and column numbers:
- ActiveCell.Offset. This method selects a cell relative to the currently active cell:
- Worksheet.Activate and then selecting a cell. If you need to select a cell on a different worksheet, first activate the worksheet, then select the cell:
- Notes 1. Avoid .Select when possible: Overuse of .Select can make your VBA code slower and harder to debug. Often, you can work directly with ranges and cells without needing to select them. For example, instead of Range("A1").Select followed by ActiveCell.Value = 5, you can simply write Range("A1").Value = 5.
- Notes 2. Screen Updating: If your code involves selecting multiple cells rapidly, turning off screen updating can significantly improve performance:
- Pay attention that parameter Target in Worksheet_Change is not a one cell, this is Range, list of cells, and each item in this cell can be empty:
We can use Debug.Print "Worksheet_Change" to check that trigger fires.
1: Sub SelectSpecificCell()
2: Range("A1").Select ' Selects cell A1
3: End Sub
4:
5: Sub SelectRangeOfCells()
6: Range("B2:C5").Select ' Selects the range B2 to C5
7: End Sub
1: Sub SelectCellByRowColumn()
2: Cells(3, 2).Select ' Selects cell B3 (row 3, column 2)
3: End Sub
1: Sub SelectCellOffset()
2: ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select ' Selects the cell one row below the active cell
3: ActiveCell.Offset(0, -1).Select ' Selects the cell one column to the left of the active cell
4: End Sub
1: Sub SelectCellOnDifferentSheet()
2: Worksheets("Sheet2").Activate ' Activates Sheet2
3: Range("A1").Select ' Selects cell A1 on Sheet2
4: End Sub
1: Application.ScreenUpdating = False
2: ' Your code here
3: Application.ScreenUpdating = True
4. Going forward - Call REST API.
Of course, I do not fully publish my commercial VBA-code for customer, as usually I show in my blog only small parts of code. Therefore since this point, sorry, will be only common recipe.
1: Sub CallRESTAPI()
2:
3: Dim objHTTP As Object, strResponse As String
4: Dim url As String
5:
6: ' Replace with your API endpoint
7: url = "your-api-endpoint-here"
8:
9: Set objHTTP = CreateObject("MSXML2.ServerXMLHTTP")
10:
11: With objHTTP
12: .Open "GET", url, False ' Asynchronous call set to False for simplicity
13: .setRequestHeader "Content-Type", "application/json" ' Adjust as needed
14: ' Add other headers like authorization if required
15: '.setRequestHeader "Authorization", "Bearer your-api-token"
16: .send
17: strResponse = .responseText
18: End With
19:
20: ' Process the response
21: Debug.Print strResponse ' View the response in the Immediate window
22: ' Or write to a worksheet cell:
23: ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1").Value = strResponse
24:
25: Set objHTTP = Nothing
26:
27: End Sub
Important points:
- Error Handling: The code lacks robust error handling. Include On Error GoTo statements and error handling routines to gracefully manage potential issues like network errors or invalid API responses.
- Asynchronous Calls: For long-running API calls, consider asynchronous requests (Open "GET", url, True). This prevents Excel from freezing while waiting for the response. You would then need to implement an event handler to process the response when it arrives.
- JSON Parsing: If the API returns JSON, use a JSON parsing library or VBA's native JSON functionality (available in later Excel versions) to extract specific data from the response.
- Authentication: Most APIs require authentication. The example shows where to add authorization headers, but the specific implementation (API keys, OAuth, etc.) will vary depending on the API.
- Method and Body (for POST, PUT): For methods other than GET, use the appropriate .Open method and provide the request body using .send (your-request-body)
- Remember to replace placeholders like "your-api-endpoint-here" with the actual details of the API you're calling. Also, consult the API documentation for specific requirements regarding headers, request body format, and authentication.
5. Going forward - call Selenium driver..
Firstly we need to install wrapper https://florentbr.github.io/SeleniumBasic/, add reference to Selenium driver, than need to download https://github.com/mozilla/geckodriver/releases and set path to it:
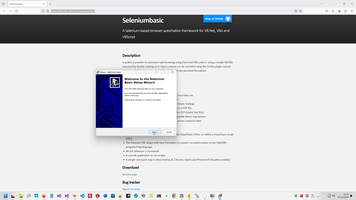
As you can see - Microsoft required from me something additional information.
Than I try to call Firefox driver from VBA:
1: Sub SeleniumFillForm()
2:
3: Dim driver As New Selenium.FirefoxDriver
4:
5: Dim FirefoxOptions As Object
6: Set FirefoxOptions = CreateObject("Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxOptions")
7: FirefoxOptions.SetBinary("C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe") 'Example path; adapt as needed
8:
9: driver.SetCapability "moz:firefoxOptions", "{""args"": [""-headless""]}", FirefoxOptions 'Optional: For headless mode
10:
11: driver.Start "firefox", "D:\Geckodriver\geckodriver.exe" , "https://www.example.com" ' Specify path here
12:
13: driver.Get "your-website-url"
14: driver.FindElementById("elementId").SendKeys "your value" & Chr(13) 'Using ID
15: driver.FindElementByName("elementName").SendKeys "your value" & Chr(13) 'Using name
16: driver.FindElementByCss("input[type='text']").SendKeys "your value" & Chr(13) 'Using CSS selector
17: driver.Quit
18:
19: End Sub
But failed.
This means library SeleniumBasic currently not working properly in VBA with Firefox, because in Node.JS and .NET environment Selenium technology working fine in the same my computer, look please to this topic My workable Selenium project templates with .NET and Node.js
We can solve this trouble with two ways (1) Create own COM-object, like any COM-object I usually created to Excel:
- My typical Excel VBA project (Excel VBA frontend can working with remote database) + admin panel (high DPI manifest).
- PDF creator COM-object based on TheArtOfDev.HtmlRenderer.PdfSharp
- How to create and testing COM-object of ancient ASP web-sites - list of tools and description of all workflow.
- Tune SQL-dbmail COM-component
- How to expand ancient ASPpage by function in Com-visible dll
- COM-component for classic ASP (eng)
Or we can try to use Chrome instead Firefox. In this case we need to use special implementation of Chrome https://googlechromelabs.github.io/chrome-for-testing/ and we can use another template:
1: Dim bot As New WebDriver
2: bot.Start "chrome", weburl
3: bot.Get "site"
4: bot.FindElementById("elementId").SendKeys "your value"
6. Why script can not started.
Of course, main troubles with VBA related to not started script. Pay attention to rules number one in Excel - after any changing of worksheet security rules you must restart Excel.
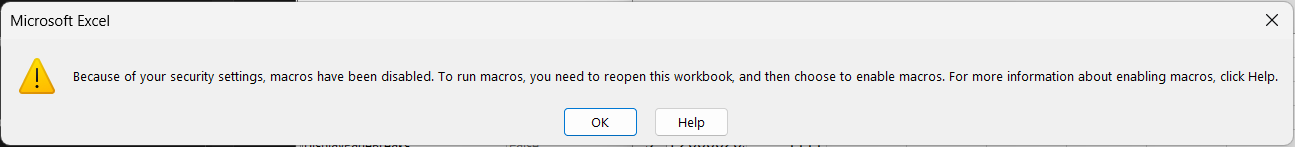
This is place where Microsoft hides most important checkpoint to enable VBA:
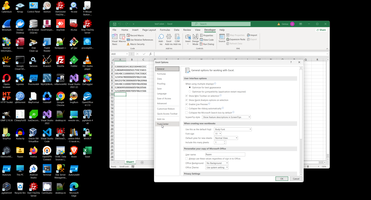
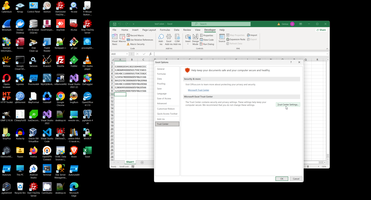
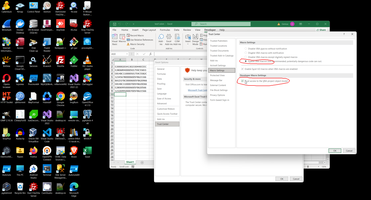
And this is not already working, look to VBA documentation:
- Digital Signatures: Even with macros enabled, a digitally signed macro from an untrusted publisher might be blocked. You might need to specifically trust the publisher of the macro. Check your Trust Center settings related to digital signatures.
- Group Policy Restrictions: If your computer is part of a corporate or organizational network, Group Policy settings might be overriding your local Excel settings and preventing macros from running. Contact your IT administrator if you suspect this is the case.
- Antivirus Software Interference: Some antivirus programs have features that can block macros, even if Excel's settings allow them. Temporarily disable your antivirus software (with caution!) to see if it resolves the issue. If so, you might need to add an exception for your Excel file or adjust your antivirus settings.
- Hidden Modules: If the VBA modules containing your macros are hidden, they might not run automatically. In the VBA editor, go to View > Project Explorer. Check if any modules have a small lock icon next to them. Right-click on any locked modules and choose View Properties. Uncheck the "Hidden" attribute on the "Protection" tab.
- Corrupted Excel Installation/File: A corrupted Excel installation or a corrupted .xlsm file could also be causing problems. Try repairing your Office installation or try the macro in a new, blank .xlsm workbook to see if it works there.
And, of course, we need to save Excel file to Macro-enabled workbook.
7. Deploy VBA code.
In most case distributing VBA code need to make just as *.XLSM (macro-enabled workbook).
If VBA function is special function what can used in any worksheet, you can deploy functions as Add-in. In this case any Add-in can deploy to special folder like C:\Users\xxxx\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\AddIns and all Add-in will be adding automatically to each workbooks. In this case Workbook must be saved with *.XLAM extension.
Also *.XLAM Add-in can be add to new worksheet manually.
Or Worksheet code can add Add-in automatically like this (StackOwerflow):
8. Transform onPage VBA script to Excel Add-in.
Any onPage VBA script can be transformed to binary Excel Add-in. We can save code as *XLAM Add-in, in this case Sheet disappeared and we can assign Add-in to any new workbook.
This common idea allow to transform any VBA code to XLAM Add-in. Events bind by name.
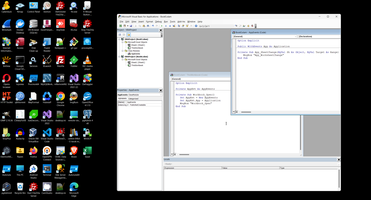
1. This is two block ob code, first is ThisWorkbook VBA code (comments generated automatically):
1: Option Explicit
2:
3: Private AppEvt As AppEvents
4:
5: Private Sub Workbook_Open()
6: Set AppEvt = New AppEvents
7: Set AppEvt.App = Application
8: MsgBox "Workbook_Open"
9: End Sub
- Private AppEvt As AppEvents: This declares a private object variable AppEvt of type AppEvents. This variable will hold an instance of your class module. Because it is declared at the module level (as opposed to within a single procedure) it is available to all event handlers within the ThisWorkbook module.
- Private Sub Workbook_Open(): This is the workbook's open event. It's where you initialize the event handling.
- Set AppEvt = New AppEvents: This creates a new instance of your AppEvents class. This is important - just declaring the variable doesn't create an instance to work with, so the 'Set' keyword here instantiates it.
- Set AppEvt.App = Application: This is the critical line that connects your event handler. It assigns the Application object to the App variable within your AppEvt instance. This establishes the link so that the App_SheetChange event in your class module is triggered by Excel's application-level sheet change event.
2. Second is AppEvents class module (comments generated automatically):
1: Option Explicit
2:
3: Public WithEvents App As Application
4:
5: Private Sub App_SheetChange(ByVal Sh As Object, ByVal Target As Range)
6: MsgBox "App_WorksheetChange"
7: End Sub
- Public WithEvents App As Application: This declares a public object variable App of type Application with event handling enabled (WithEvents). This is crucial for catching application-level events. Declaring it as Public exposes this object to the other modules within your project.
- Private Sub App_SheetChange(...): This is the event handler. It will be triggered whenever the Application.SheetChange event fires (i.e., a sheet is changed anywhere in Excel while the add-in is loaded). The Sh parameter represents the sheet that changed, and Target represents the range of changed cells.
9. Digital sign VBA code.
To reduce various security alert best way is sign VBA script. In my case I have prepared certificate.
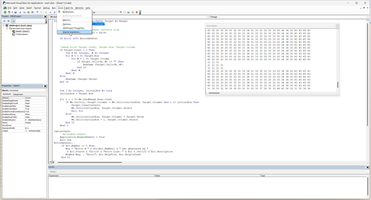
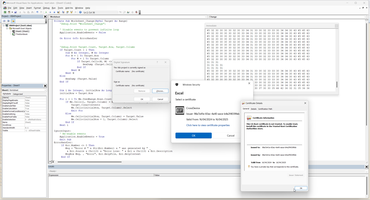
There are three way to update self-signed certificate, first is simplest.
-
# SelfCert.exe /n "Organization"

-
#PowerShell# New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type CodeSigningCert -Subject "CN=MyCompanyName" -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My"
-
# makecert.exe
Excel context:
 )
)
|
|